The medieval period, also known as the feudal era in Europe, was a tumultuous historical phase marked by numerous battles and wars. Medieval ancient weapons not only reflected combat techniques but also showcased the cultural and societal development of nations. In this article, alongside Pywar, we explore the most prominent ancient combat weapons, their profound influence on the history of warfare, and their roles in shaping the outcomes of critical battles.
Longsword
The longsword was the most common weapon of medieval knights. Originating in 13th-century Europe, the longsword, with a length ranging from 90 to 120 cm, allowed its wielder flexibility in both attack and defense. Often used in close-combat battles, it required advanced skill from the swordsman. One famous battle where the longsword was employed was the Battle of Hastings in 1066, which marked the end of the Anglo-Saxon dynasty and the beginning of Norman rule in England.

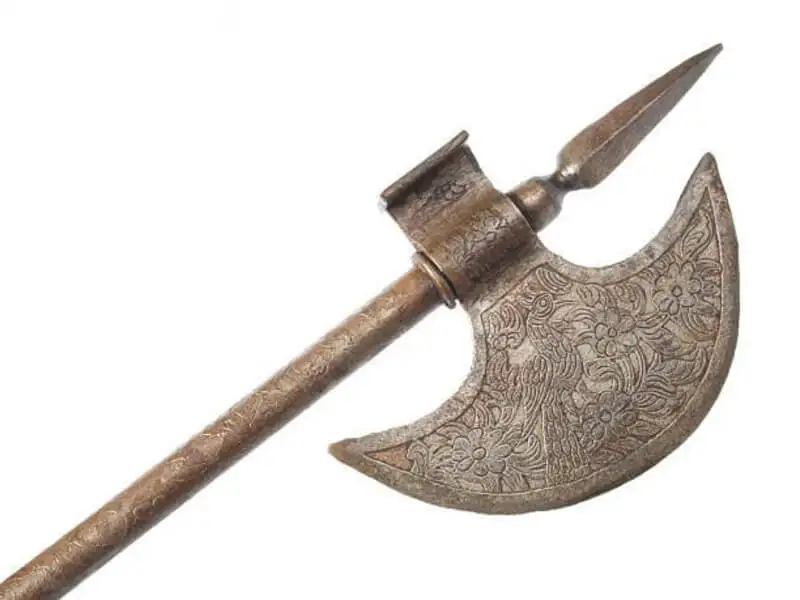
Battle Axe
The battle axe was not only a weapon but also a symbol of power. This ancient weapon could feature one or two blades, making it ideal for slashing through armor and disrupting enemy ranks. Frequently wielded by Viking and Germanic warriors, the battle axe saw significant development in 8th-century Northern Europe and was used in renowned battles like the Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, where Viking warriors attempted to invade England.

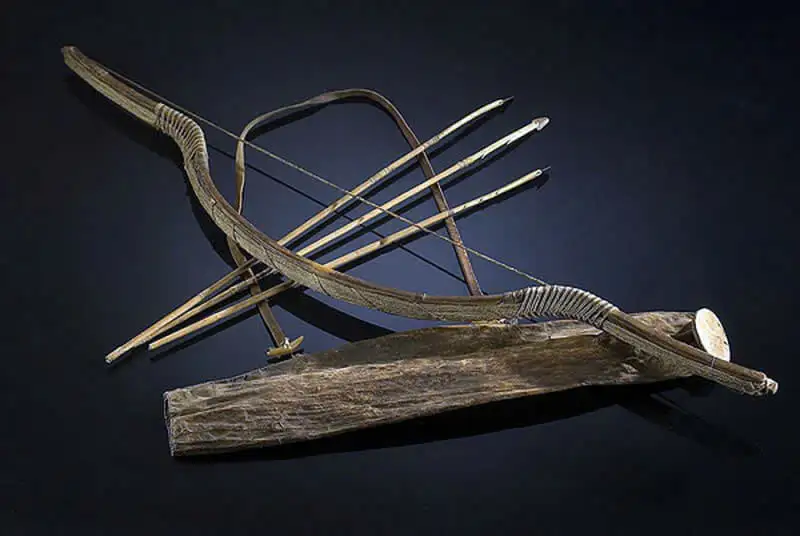
Bow and Arrow
The bow and arrow were crucial long-range weapons in medieval battles. With their rapid and accurate firing capabilities, they enabled armies to maintain flexibility and exert constant pressure on opponents. The English longbow, renowned for its strength and versatility, was developed in 12th-century England and widely used in the Battle of Agincourt in 1415, a famous encounter in the Hundred Years’ War between England and France.

Pike
The pike, a weapon ranging from 4 to 5 meters in length, was used to counter cavalry and spearmen. With its sharp tip, the pike formed a defensive barrier to halt cavalry charges, creating opportunities for other army units to strike. Developed in 15th-century Europe, the pike proved effective in battles like the Battle of Pavia in 1525, where Spanish forces defeated the French through its strategic use.

Chainmail
While not strictly a weapon, chainmail was an essential part of a medieval warrior’s combat gear. Originating in ancient Rome and becoming widespread in medieval Europe, chainmail offered protection against close-combat ancient weapons like swords, axes, and spears while keeping warriors agile in battle. It was used in notable battles such as the Battle of Waterloo in 1815, though this occurred near the end of the medieval period.

Flanged Axe
The flanged axe was a specialized weapon designed to penetrate armor. Featuring an axe blade on one side and a hammer on the other, it provided versatility in attacking and breaking through enemy defenses. Developed extensively in 14th-century Europe, the flanged axe proved its worth in battles like the Battle of Crécy in 1346, where it effectively shattered the armor of cavalry units.

Spear
The spear is one of the most classic and widespread ancient weapons in warfare history. Used since prehistoric times and further refined in the medieval era, the spear’s ability to strike from a safe distance made it a staple for most medieval armies against cavalry and infantry. It featured in numerous historic battles, including the Battle of Hastings in 1066 and the Battle of Agincourt in 1415.

Dagger
The dagger was a vital secondary weapon, often used in duels or close-combat situations. It allowed warriors to strike swiftly when longswords or battle axes were impractical. Widely used since the 10th century in Europe, the dagger also served as a multipurpose tool for medieval warriors, from cutting grass to opening containers. It appeared in battles like the Battle of Stirling Bridge in 1297 during the Scottish-English wars.

Falchion
The falchion, a curved-blade weapon combining traits of a sword and an axe, was developed in 13th-century Europe. Its versatility in slashing and thrusting made it suitable for both long-range and close combat. Favored by many medieval warriors for its unique design and powerful cutting ability, the falchion was used in famous battles like the Battle of Falkirk in 1298 during the Scottish-English wars.

Crossbow
The crossbow was a powerful projectile weapon capable of piercing armor. With its automatic bolt-loading mechanism, it allowed for continuous and more precise shots compared to traditional bows. Extensively developed in 11th-century Europe, the crossbow played a key role in decisive medieval battles, notably the Battle of Agincourt in 1415, where English forces used it to break through French defenses.
Conclusion
Medieval ancient weapons were not merely tools of war but also symbols of power and combat ingenuity. The top 10 medieval combat weapons we’ve explored reflect not only advancements in weapon technology but also the diversity and richness of military tactics throughout history. Understanding these weapons offers deeper insight into historical battles and the pivotal roles they played in determining their outcomes.




